Document Capture
Available Document Frames
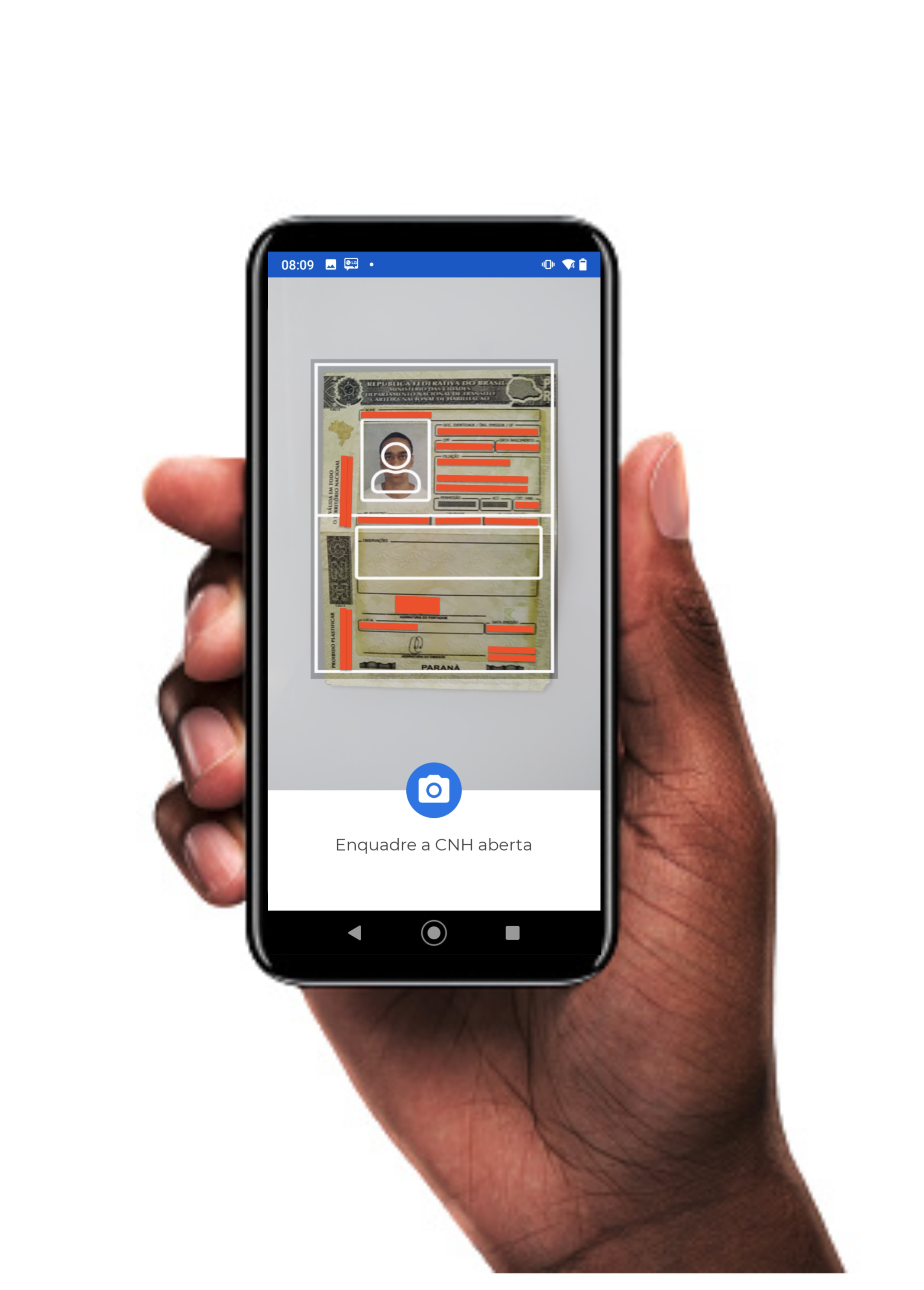
In this camera mode, there is a capture frame to assist the user in positioning the document correctly. Once the document is correctly positioned, the user must click the button to capture the photo of the document.
The SDK does not perform any type of validation on what is being captured.
In this camera mode, it is possible to capture the following documents:
CPF: Capture the front of the CPF;
CNH: Capture the open CNH;
CNH Front: Capture the front of the CNH;
CNH Back: Capture the back of the CNH;
RG Front: Capture the front of the RG;
RG Back: Capture the back of the RG;
Others: Capture any other document.
Initializing the SDK
Create an instance of the builder (generated through the IAcessoBioBuilder interface), providing the relevant context and the implementation of the AcessoBioListener class as parameters.
The implementation of this class is quite simple and can be done with just a few lines of code. All you need to do is instantiate the builder by specifying the context and override the callback methods with the business logic of your application:
Implementing Callback Functions
Note that the work of implementing the AcessoBioListener class is largely about configuring the callback methods. Each method is called in a specific situation based on the SDK's return.
Simply override the methods shown in the previous step with your application's business logic:
onErrorAcessoBio(ErrorBio errorBio)
This method is invoked with a parameter of type ErrorBio, which contains details about the error. Learn more about the ErrorBio type in the error handling section.
onUserClosedCameraManually()
This method is invoked whenever the user manually closes the camera, such as by clicking the "Back" button.
onSystemClosedCameraTimeoutSession()
This method is invoked as soon as the maximum session time is reached (without capturing any image).
It can be configured in the builder through the setTimeoutSession method. This method should receive the maximum session time in seconds. You can change the maximum session time for your user when using the face detection feature (Selfie camera with smart capture). If the user exceeds the time set in your process to capture the photo, you can display a customizable message or instruction to the user. The default value is 40 seconds, and the minimum value is also 40 seconds.
onSystemChangedTypeCameraTimeoutFaceInference()
This method is invoked as soon as the maximum time for detecting the user's face is reached (without detecting anything). In this case, the camera mode is automatically switched to manual capture mode (without the smart capture outline).
The maximum capture time when using face detection (Selfie camera with smart capture) is 13 seconds. If the user encounters difficulty capturing the photo through face detection and exceeds the time set in the process, the capture is automatically switched to manual mode, aiming to make the action easier for the user (TimeoutToFaceInference).
All the above methods must be created as indicated in your project (even without any logic). Otherwise, the project will not compile successfully.
Implementing Listeners for Camera Events
The implementation of these listener methods must be done through an instance of the iAcessoBioSelfie class.
The camera opening method, which is called in the next step, needs to know what to do when it successfully captures an image or when an error occurs in the process. It is necessary to inform "what to do" to the camera opening method by implementing listeners that are called in cases of success or error.
Through the configuration of the listeners, you can specify what happens in your app in error situations (onErrorDocument method) or success situations (onSuccessDocument method) during image capture.
The example below illustrates the configuration of the listeners, building, and opening of the camera:
Prepare and open the camera
It is necessary to create an instance of the builder using the build() method. This method is provided through the object generated with the IAcessoBioBuilder interface and the AcessoBio class:
The next step is to prepare the camera using the prepareDocumentCamera() method with the object returned by the builder (named UnicoCheckCamera in the example above).
The prepareDocumentCamera() method generates an object of type UnicoCheckCameraOpener.Document, which is used to open the camera with its open() method, receiving the parameters for the type of document to be captured, which are:
DocumentCameraType.CPF
Frame for capturing the front of the CPF.
DocumentCameraType.CNH
Frame for capturing the open CNH.
DocumentCameraType.CNH_FRENTE
Frame for capturing the front of the CNH.
DocumentCameraType.CNH_VERSO
Frame for capturing the back of the CNH.
DocumentCameraType.RG_FRENTE
Frame for capturing the front of the RG.
DocumentCameraType.RG_VERSO
Frame for capturing the back of the RG.
DocumentCameraType.None
Frame for capturing any other document.
If you need to capture a document for which we don't have a specific frame (e.g., RNE, among others), use the DocumentCameraType.None frame, which will provide you with a generic, rectangular frame that can be used to guide any capture.
onSucessDocument Method
onSucessDocument MethodWhen an image capture is successful, this method is invoked and returns an object of type ResultCamera, which is later used in the REST API calls:
The ResultCamera object returns two attributes: base64 and encrypted:
The
base64attribute can be used if you want to display a preview of the image in your app.Both the
encryptedandbase64attributes can be sent in the REST API calls to by Client.
If it's necessary to convert base64 to bitmap, the standard method doesn't work for Android. You need to perform a split at the comma (,) for it to work. If you'd like to learn more, read the article How to convert a Base64 string into a Bitmap image to show it in an ImageView?.
onErrorDocument Method
onErrorDocument MethodWhen an error occurs during image capture, this method is invoked and returns an object of type ErrorBio:
Learn more about the ErrorBio types in the error handling section of the SDK.
Making a POST Request to the Client API
Capturing the images is just the first part of the journey. After capturing the image, it is necessary to send the base64 generated by the SDK to the by Client REST APIs.
Last updated
Was this helpful?